The Brief Overview Earth's atmosphere is a jacket of gases that surrounds our planet It keeps us warm, gives us oxygen to breathe, and it is where our weather happens What Is the Greenhouse Effect?Heat emitted from Earth's surface is absorbed by gases in the atmosphere and then reradiated back to the surface Here 100 energy units = 556e24J/year, the total annual solar energy received averages 342 W/m^@ over theActivity 11 Understanding the Greenhouse Effect Grades 7 – 9 Description In Part 1 Modeling the Greenhouse Effect, students will do a lab that demonstrates the greenhouse effect, and will discuss the results of the lab In Part 2 The Earth's Energy Balance, students will color in a diagram, answer opinion

The Greenhouse Effect Niwa
Greenhouse effect diagram drawing
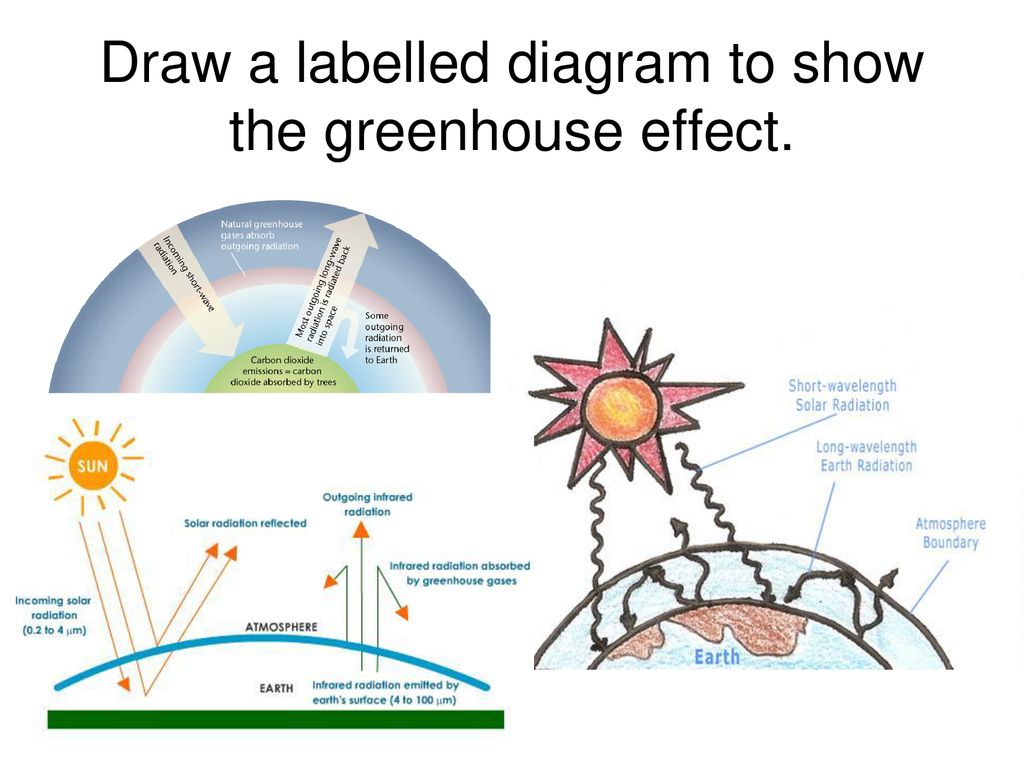
Greenhouse effect diagram drawing-The Greenhouse Effect Task Easy Draw a labeled diagram to model your teacher's description of the greenhouse effect Sunlight passes through the Earth's atmosphere and warms the Earth's surface The heat is radiated back towards space Most of the outgoing heat is absorbed/trapped by greenhouse gas molecules in the Earth's atmosphere Drawing shows four different levels of ozone in the atmosphere At top of stratosphere, 30 miles high, ozone absorbs most of the harmful ultraviolet radiation from the Sun At the top of the troposphere, 12 miles high, ozone acts as a greenhouse gas, trapping heat



Q Tbn And9gcq08vt3peivox73u6mxf7twlz Qn8btv6k1j63tcrzr0dethzt4 Usqp Cau
Greenhouse effect and explore natural and humancaused greenhouse gas emissions and their impacts Students will brainstorm and then research natural and human activities that contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and draw them in a diagram Students then discuss how they can reduce their contributions to greenhouse gas emissionsAsk students to draw a diagram illustrating the greenhouse effect Illustrate or list actions that influence carbon dioxide emissions into the atmosphere both positively and negatively NeedsWhat Causes Air Pollution?
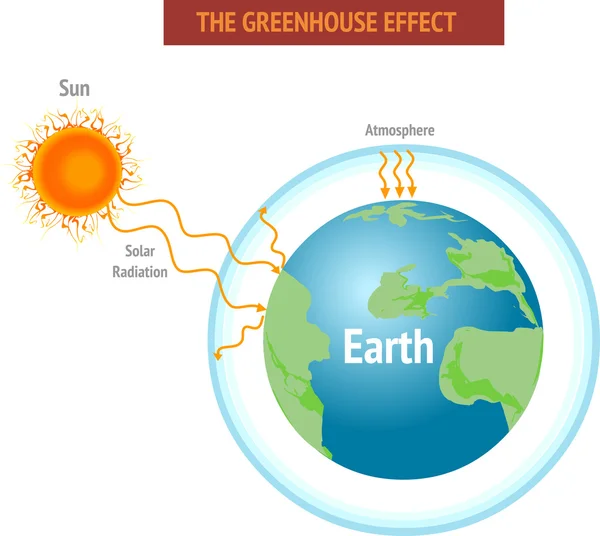
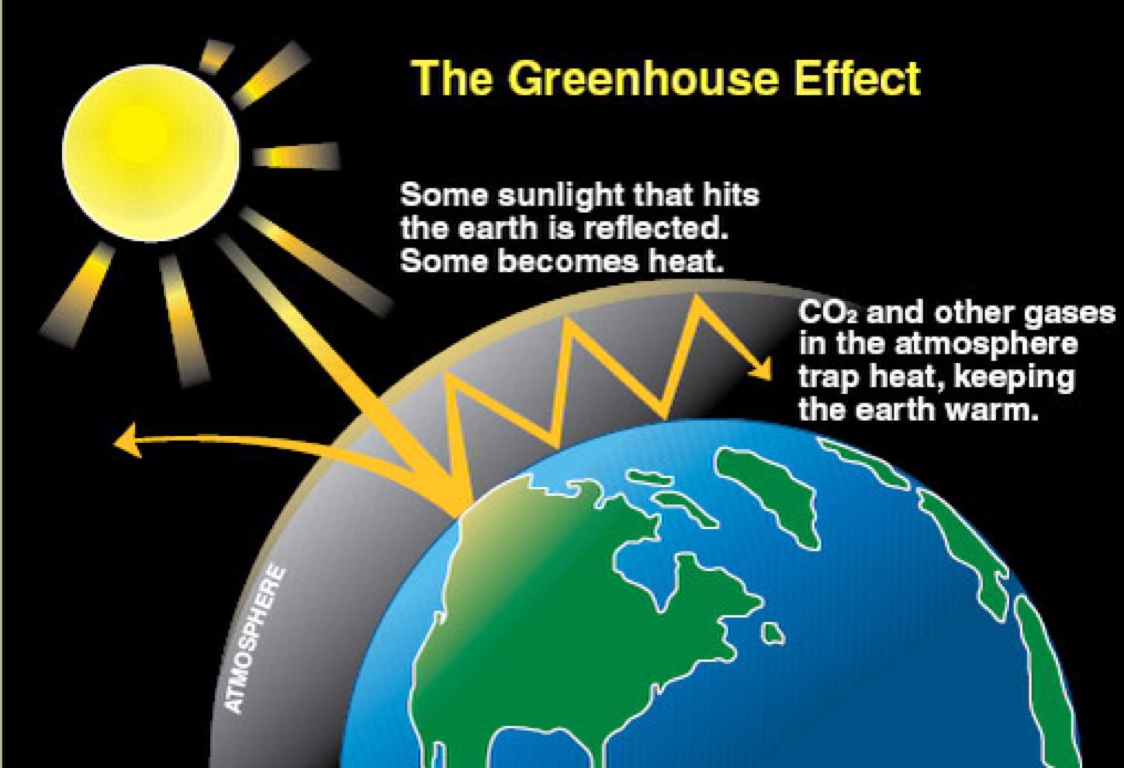
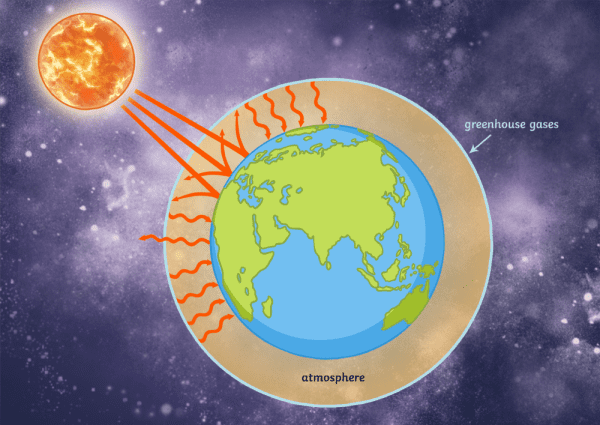
The greenhouse effect is a warming of Earth's surface and the air above it It is caused by gases in the air that trap energy from the sun These heattrapping gases are called greenhouse gases The most common greenhouse gases are water vapor, carbon dioxide, and methane Without the greenhouse effect, Earth would be too cold for life to existThe Greenhouse Effect The picture below shows the greenhouse effect Light from the sun passes through the atmosphere and is absorbed by the Earth's surface, warming it Greenhouse gases, like carbon dioxide, act like a blanket, trapping heat near the surface and raising the temperature It is a natural process that warms the planet"A greenhouse gas (sometimes abbreviated GHG) is a gas in an atmosphere that absorbs and emits radiation within the thermal infrared range This process is the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect The primary greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone
Find Greenhouse Effect Diagram Showing How Greenhouse stock images in HD and millions of other royaltyfree stock photos, illustrations and vectors in the collection Thousands of new, highquality pictures added every dayThe greenhouse effect is the process thanks to which Earth has a higher temperature than it would have without it The gases that radiate heat also known as greenhouse gases absorb the energy radiated out by the Earth and reflect a part of it back to Earth Of all the energy that the Earth receives from the Sun, a part of it around 26% isWhat's in the Atmosphere?




Example Of Student Drawing Based On Textbook Diagram Download Scientific Diagram



I What Are The Consequences Of Global Warming Ii Draw A Labelled Diagram To Show Water Cycle In Nature Iii Why Is Water Essential For Life Biology Topperlearning Com Ff5whc299
Greenhouse effect infographic vector image on VectorStock April 21 Saved by VectorStock 12 Greenhouse Effect Earth Surface Web Design Graphic Design Natural Disasters Climate Change Adobe Illustrator Vector Free Infographic The greenhouse effect is a good thing It warms the planet to its comfortable average of 59 degrees Fahrenheit (15 degrees Celsius) andSulfur hexafluoride (SF 6) is an extremely potent greenhouse gas SF 6 is very persistent, with an atmospheric lifetime of more than a thousand years Thus, a relatively small amount of SF 6 can have a significant longterm impact on global climate change SF 6 is humanmade, and the primary user of SF 6 is the electric power industry Because of its inertness and dielectric properties, it is




Greenhouse Effect Illustrations And Clipart 2 293 Greenhouse Effect Royalty Free Illustrations And Drawings Available To Search From Thousands Of Stock Vector Eps Clip Art Graphic Designers




Greenhouse Effect Vector Illustration Diagram Stock Vector Illustration Of Design Emission
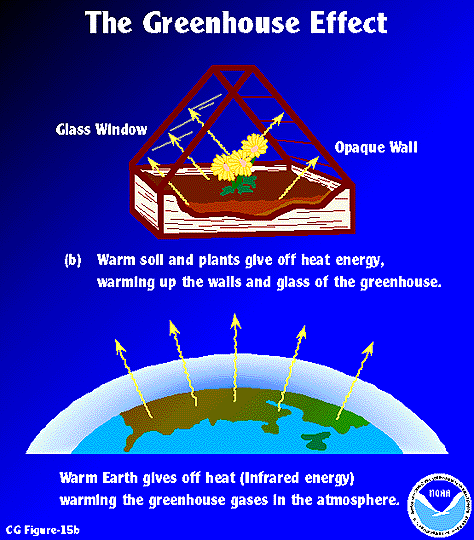
The greenhouse effect works much the same way on Earth Gases in the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide, trap heat similar to the glass roof of a greenhouse These heattrapping gases are called greenhouse gases During the day, the Sun shines through the atmosphere Earth's surface warms up in the sunlightThe greenhouse effect is a warming of the earth's surface and lower atmosphere caused by substances such as carbon dioxide and water vapour which let the sun's energy through to the ground but impede the passage of energy from the earth back into space Energy emitted from the sun ("solar radiation") is concentrated in a region of shortPlus, get full access to a library of over 316 million images Learn more Royaltyfree stock vector ID Greenhouse effect vector illustration diagram Environment pollution problem and fighting climate change Informational infographic for education and rising awareness Human industrial activity issue




Figure 3 Student Representation Of The Greenhouse Effect Oxford Research Encyclopedias



1 436 Greenhouse Effect Vector Images Free Royalty Free Greenhouse Effect Vectors Depositphotos
Ask participants to draw a diagram of the greenhouse effect based on what they know Hint participants should include sunlight, heat, Earth, Atmosphere, and Greenhouse Gases (Optional) Review together & print some GHG superheroes cards Get set!Greenhouse Effect Definition "Greenhouse effect is the process by which radiations from the sun are absorbed by the greenhouse gases and not reflected back into space This insulates the surface of the earth and prevents it from freezing" What is the Greenhouse Effect? Create your own unique sketch illustrating how Earth's Greenhouse Effect works You may handdraw your diagram or create something on the computer Either option must be a unique creation (ie DO NOT COPY & PASTE) If you choose to handdraw your diagram you will need to scan and upload your diagram into Blackboard Creativity is encouraged




Figure 3 From A Content And Language Integrated Learning Clil Project Opportunities And Challenges In The Context Of Heritage Language Education Semantic Scholar



What Is The Greenhouse Effect Can You Explain With The Help Of A Diagram Quora
Bitly/AITGHE Draw an annotated diagram explaining the Greenhouse Effect (draw the earth, not a greenhouse) (begin clip ~052) bitly/AITGHE What is the difference between Climate change and the Natural Greenhouse Effect?Greenhouse gases let the sun's light shine onto the Earth's surface, but they trap the heat that reflects back up into the atmosphere In this way, they act like the insulating glass walls of a greenhouse The greenhouse effect keeps Earth's climate comfortable Without it, surface temperatures would be cooler by about 33 degrees CelsiusStudents read to create an initial conceptual model of the greenhouse effect They then collect temperature data from a physical demonstration simulating atmospheres with and without greenhouse gases and calculate and compare the mean, median, and range Finally, they revise their model of the greenhouse effect using their data analysis and an interactive



Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect
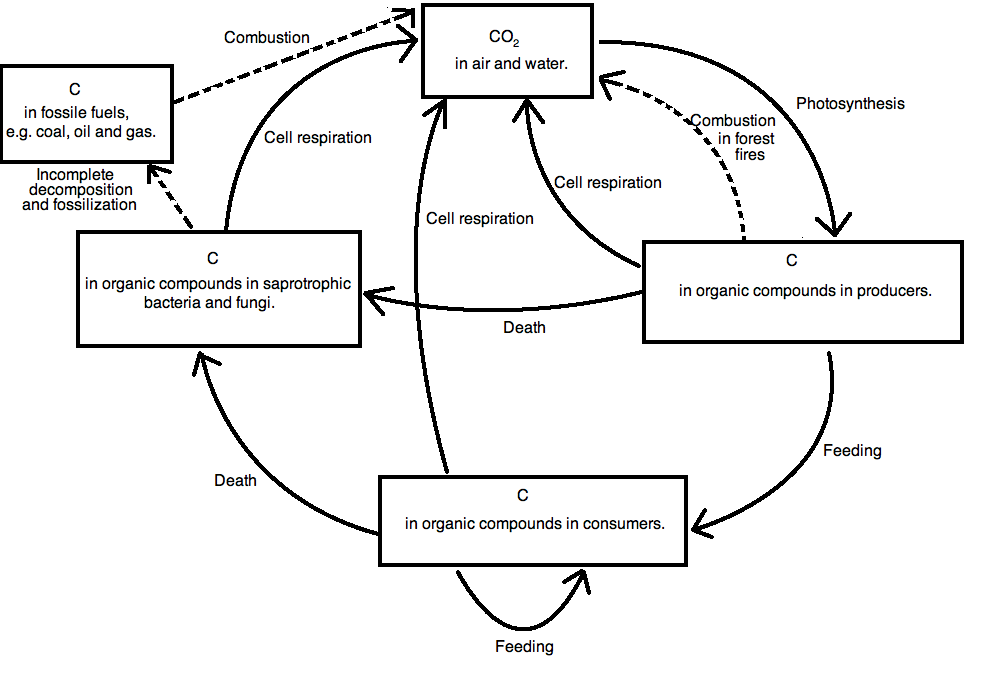
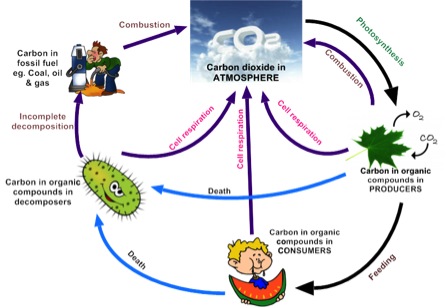
How does the Enhanced Greenhouse Effect relate to these?Draw a diagram and label to EXPLAIN the greenhouse effect The greenhouse effect is a process that warms the atmosphere due to the absorption of radiation from the greenhouse gases Explain how the Carbon Cycle is involved in global climate changeOrganize them in a chart below 5




Greenhouse Gases Easy Drawing Novocom Top



The Greenhouse Effect
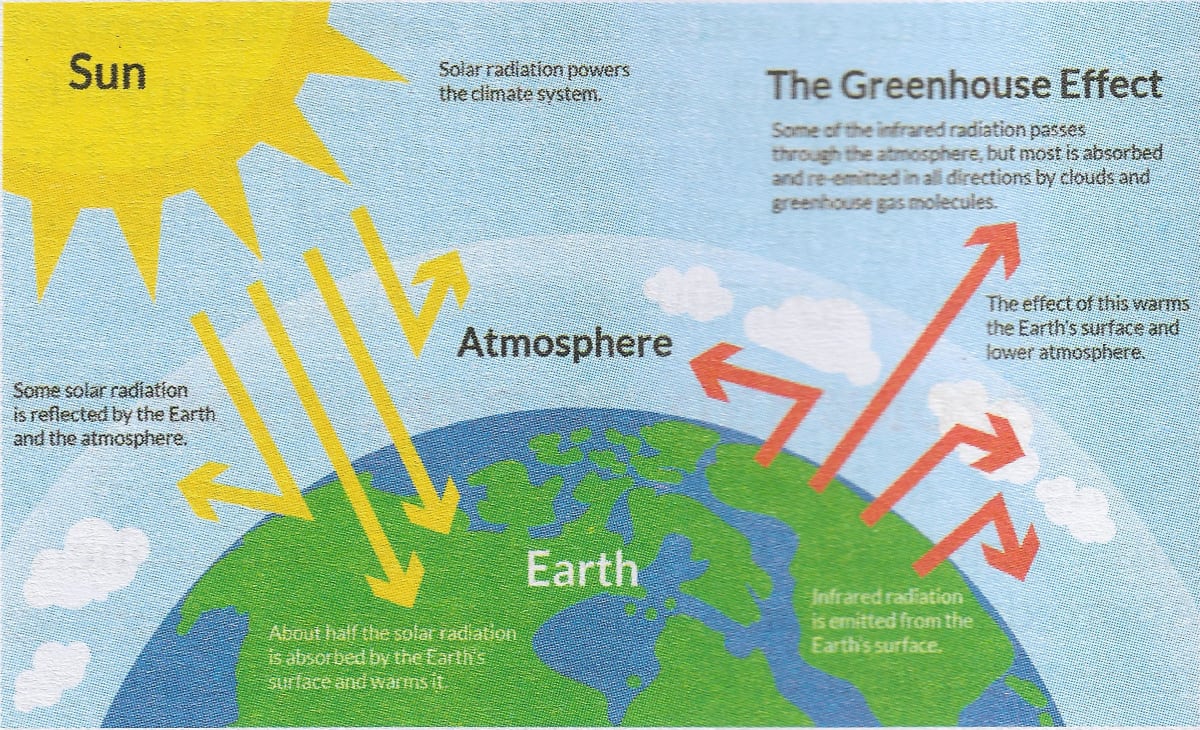
(also in R&B textbook)The diagram gives more details about this process, called the greenhouse effect How the greenhouse effect works electromagnetic radiation at most wavelengths passes through the Earth's atmosphereEarth's greenhouse effect is basic to understanding global warming Like many natural processes, this effect is best understood in terms of energy flows For starters, Figure 6 shows the energy flow near the surface of an imaginary Earth that has no greenhouse gases (these are trace gases, mainly water vapor and CO 2 ) but has an otherwise



Lab 2 Climate And Earth S Energy Balance



Www Manhassetschools Org Cms Lib8 Ny Centricity Domain 709 Greenhouse student Pdf
Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Introduction The enhanced greenhouse effect refers to human activities that are adding to the warming of the atmosphere due to the greenhouse effect—the presence of gases that increases the atmosphere's retention of the heat energy of the sun The burning of fossil fuels including coal, oil, and natural gas, along with the clearing of land forThe atmosphere protects life on Earth by absorbing ultraviolet solar radiation, warming the surface through heat retention (greenhouse effect), and reducing temperature extremes between day and night (the diurnal temperature variation) The common name given to the atmospheric gases used in breathing and photosynthesis is airGreenhouse effect diagram can either be printed off or projected and used to explain the Greenhouse effect



Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia



3zrenqno37z Vm
How the Greenhouse works and what does it doYou can edit this template and create your own diagram Creately diagrams can be exported and added to Word, PPT (powerpoint), Excel, Visio or any other document Use PDF export for high quality prints and SVG export for large sharp images or embed your diagrams anywhere with the Creately viewerGreenhouse effect, a warming of Earth's surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapor has the largest effectA greenhouse is a house made of glass that can be used to grow plants




How To Draw A Diagram Of Green House Effect Global Warming Easy Youtube




Greenhouse Atmosphere Let S Heat Things Up Lesson Ciencias Naturales Ciencia Dieta Balanceada
2 Draw a diagram below showing how thermal radiation strikes Earth Use it to explain why the equator has the largest amount of solar radiation 3 What are the three spheres that are part of the biosphere – give a characteristic of each one 4 What are the 6 main Canadian biomes?Energy industry Environmental impact Wikipedia The Energy resources diagram example was created in the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software using the Manufacturing and Maintenance solution from the Illustration area of ConceptDraw Solution Park Flowchart Of Greenhouse Effect Graphic A simplified animation of the greenhouse effect Perhaps the most impressive of cloud formations, cumulonimbus (from the Latin for "pile" and "rain cloud") clouds form due to vigorous convection (rising and overturning) of warm, moist and unstable air




1 Which Arrow In The Diagram Above Shows The Greenhouse Effect 2 Describe The Direction Of The Brainly Ph




What Is Green House Effect B Draw A Well Labeled Diagram Of Carbon Cycle Brainly In
The greenhouse effect is the process by which radiation from a planet's atmosphere warms the planet's surface to a temperature above what it would be without this atmosphere Radiatively active gases (ie, greenhouse gases) in a planet's atmosphere radiate energy in all directionsPart of this radiation is directed towards the surface, thus warming itHow are they related?The two large flows on the right represent a kind of energy recycling program that constitutes the greenhouse effect;




The Greenhouse Effect Easily Understood With A Diagram Help Save Nature




Diagram Of Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Diagram
Diagram Of Greenhouse Effect Saved by Yasar alp Ozturk 1 Greenhouse Effect Heat Energy Red Glass Worksheets Diagram Architecture Arquitetura Thermal Energy Literacy CentersActivity 12 Understanding the Greenhouse Effect Grades 5 – 6 Description In Part 1 Modeling the Greenhouse Effect, students will complete a lab that demonstrates the greenhouse effect and will discuss the results of the lab In Part 2 Earth's Energy Balance, students will color in a diagram, answer opinion questions, and perform a skit1 Example of student work about exploring the greenhouse effect in garden greenhouses Greenhouse effect (Figure 411) is a sketch of the experiment done in class FIG 411 Student drawing of model of the greenhouse effect in a garden greenhouse The student labeled two lamps shining on two clear plastic tubs



The Greenhouse Effect Draw And Label A Diagram Of The Carbon Cycle Do It Now Ppt Download




The Greenhouse Effect Easily Understood With A Diagram Help Save Nature Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases Earth Surface
Ask them to draw, by themselves, an annotated diagram to explain the greenhouse effect Activity stage 2 Divide students into pairs Ask them to Compare their diagrams Justify their ideas, where there are differences Agree a common diagram which they draw on an OHT or produce a PowerPoint slide Plenary Bring together students in aInformation on the Greenhouse Gas Effect Include the definition of the greenhouse gas effect Include 5 facts about the greenhouse gas effect This information should all be typed and printed out Data Table, Graphing Sheet and Conclusion Questions paper on your poster Type up your information so it looks professional and print"A greenhouse gas (sometimes abbreviated GHG) is a gas in an atmosphere that absorbs and emits radiation within the thermal infrared range This process is the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect The primary greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone



Lesson Ppt Download




How To Explain The Greenhouse Effect To Kids With Printables Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases Effect Greenhouse Gases
Off the surface is absorbed and reradiated into the atmosphere, where much of it is absorbed by the greenhouse gases This is known as the greenhouse effect BACKGROUND Use the following terms to label the diagram belowGreenhouse diagram ( Flowchart) Use Creately's easy online diagram editor to edit this diagram, collaborate with others and export results to multiple image formats We were unable to load the diagram You can edit this template and create your own diagram Creately diagrams can be exported and added to Word, PPT (powerpoint), Excel, Visio orThe greenhouse ventilation system also has a large effect on infiltration Inlet and outlet fan shutters often allow a large air exchange if they do not close tightly due to poor design, dirt, damage or lack of lubrication Window vents seal better than inlet shutters, but even they require maintenance to ensure a tight seal when closed




Greenhouse Effect Teaching Box Ucar Center For Science Education




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica
The greenhouse effect is generally modeled on a macro scale by designating energy balance for the planetary system This involves the incoming solar radiation, reflected solar energy, absorbed solar energy at the ground, and subsequent reradiation at longer wavelengths from the ground The reradiated energy is then either transmitted out of the system or absorbed by the greenhouseGo outside Put a small circle in the middle of a field to represent EarthEnergy resources diagram "Consumption of energy resources, (eg turning on a light) requires resources and has an effect on the environment Many electric power plants burn coal, oil or natural gas in order to generate electricity for energy needs While burning these fossil fuels produces a readily available and instantaneous supply of



What Is The Difference Between The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Socratic




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids




Essay On Greenhouse Effect For Students 500 Words Essay




Atmosphere Climate Environment Information Programme



Http Www Cosee Net Cosee West Lessonplans Climate change lesson plans Greg watkevich Global warming and greenhouse effect Pdf




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia



What Are Greenhouse Gases Answered Twinkl Teaching Wiki




Iv Using Central Ideas About Light And Thermal Phenomena To Explain The Greenhouse Effect Exploring Physical Phenomena




Teaching Climate Change American Federation Of Teachers



5 2 The Greenhouse Effect Bioninja




The Greenhouse Effect Niwa




What Is Greenhouse Effect Definition Causes And Effects




What Is Green House Effect B Draw A Well Labeled Diagram Of Carbon Cycle Brainly In




Iv Using Central Ideas About Light And Thermal Phenomena To Explain The Greenhouse Effect Exploring Physical Phenomena




Textbook Representation Of The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gas Layer Download Scientific Diagram



Untitled Document



Week 6 1 The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect




The Greenhouse Effect The Atmosphere Siyavula




The Diagram Given Shows The Green House Effect Which Of The Following Would Have Been In The Absence Of Greenhouse Effect In The Atmosphere




Natural And Human Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Diagram Showing Solar Radiation And Planet Earth Global Warming Climate Change Canstock




2 Schematic Of The Greenhouse Effect From 16 Download Scientific Diagram



Www Chicagobotanic Org Downloads Nasa Unit 1 Grades 7 9 Activity 1 1 Understandingthegreenhouseeffect Pdf



Q Tbn And9gcq08vt3peivox73u6mxf7twlz Qn8btv6k1j63tcrzr0dethzt4 Usqp Cau



1



Ib Biology Notes 5 2 The Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Effect Diagram High Res Stock Images Shutterstock




Esther Badu Kwarteng Badukwarteng Profile Pinterest




5 2 1 Draw And Label A Diagram




What Is Green House Effect B Draw A Well Labeled Diagram Of Carbon Cycle Brainly In
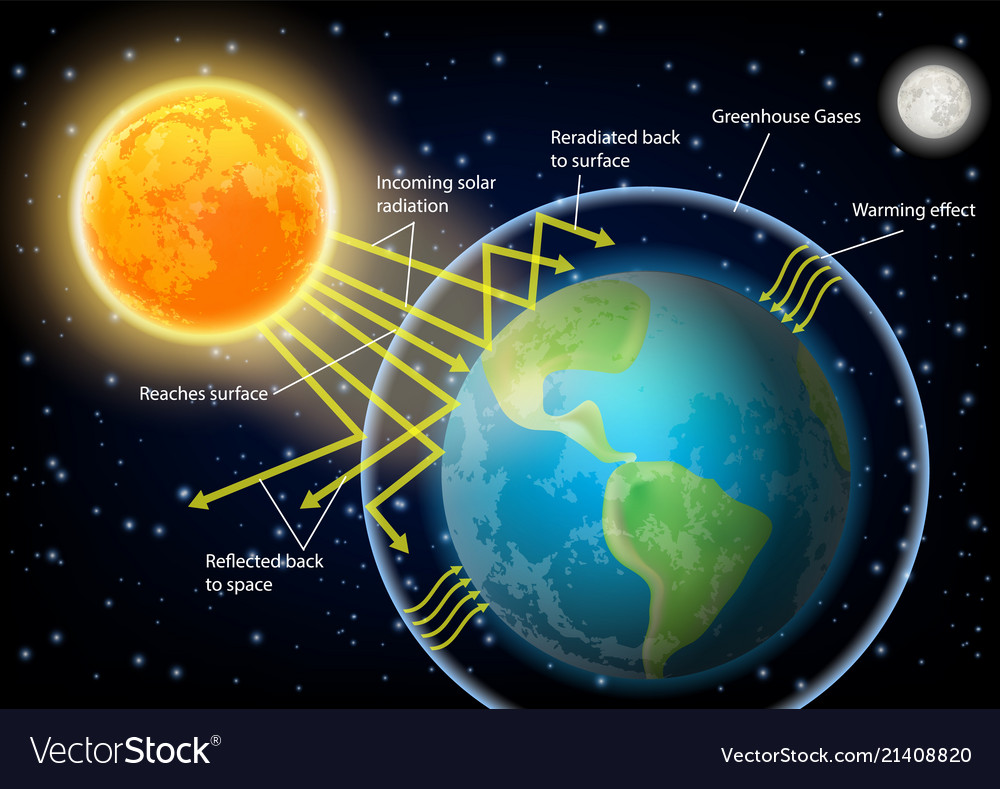



Greenhouse Effect Diagram Royalty Free Vector Image



Mare Lawrencehallofscience Org Sites Mare Lawrencehallofscience Org Files Images Science Briefing Climate Change 15 Pdf




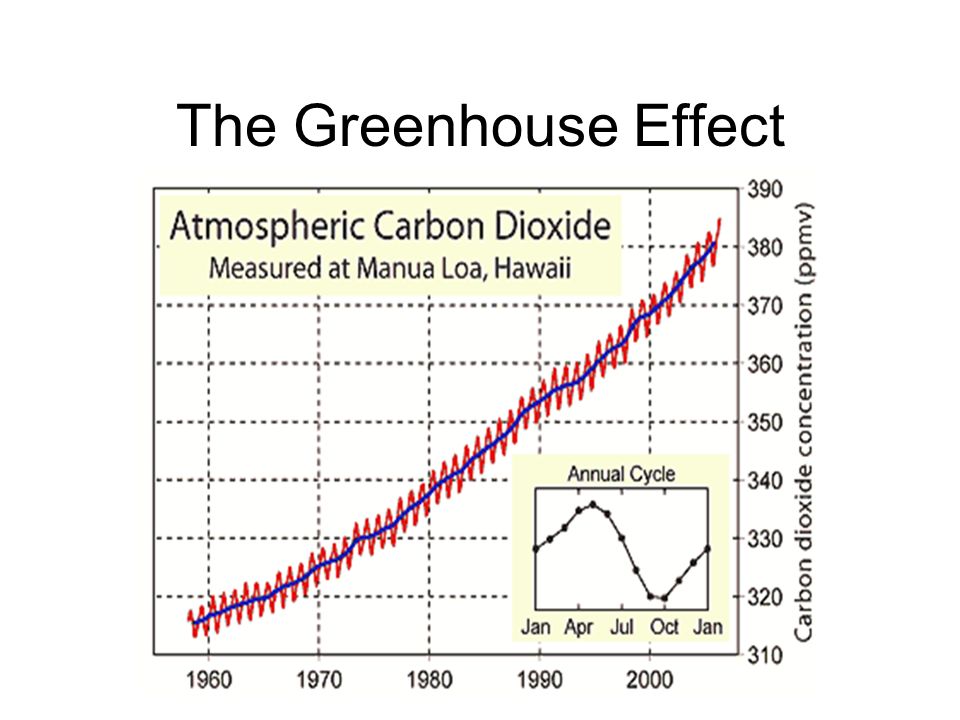
Co2 The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming From The Pioneering Work Of Arrhenius And Callendar To Today S Earth System Models Sciencedirect



Q Tbn And9gctoyncs8qyvzsnlf0ehywfdbiqsqkgodl5exlpxd0mjwanu7ugb Usqp Cau
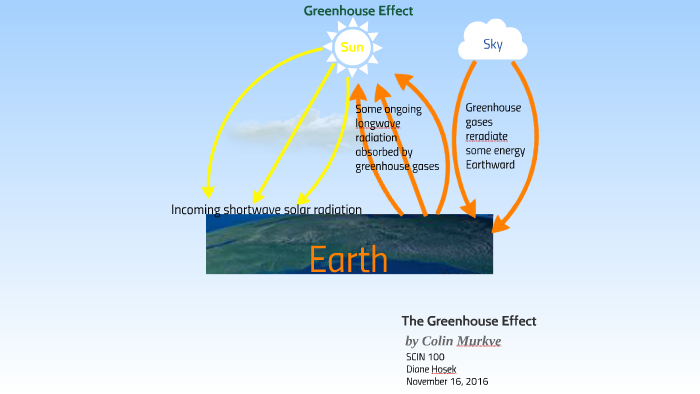



Greenhouse Effect Sketch By Colin Murkve



The Carbon Cycle And Greenhouse Effect Apes By Reymond P
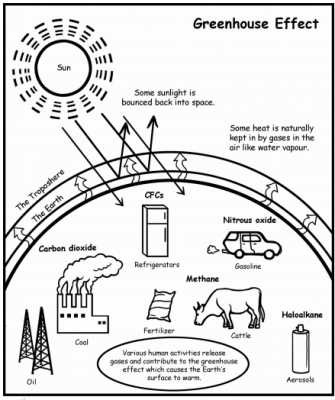



Greenhouse Effect Clever Cookies



The Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Effect Diagram Efecto Invernadero Ciencias De La Tierra Y Calentamiento Global




What Are Greenhouse Gases Answered Twinkl Teaching Wiki



The Greenhouse Effect



5 2 The Greenhouse Effect Bioninja
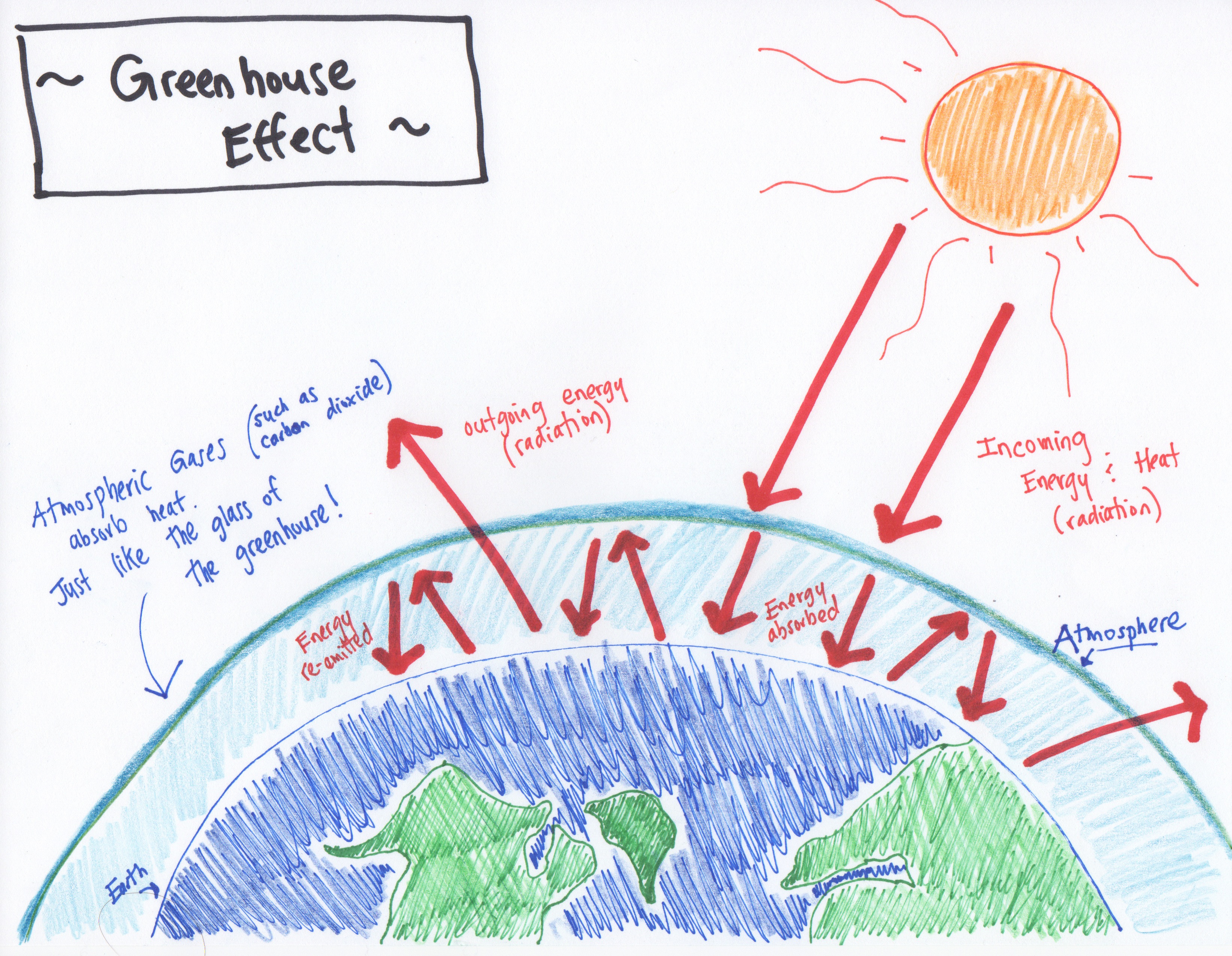



Climate Change Silence Is Ignorance Really Bliss Early Career Ecologists
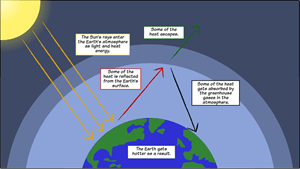



Creating A Greenhouse Effect Diagram
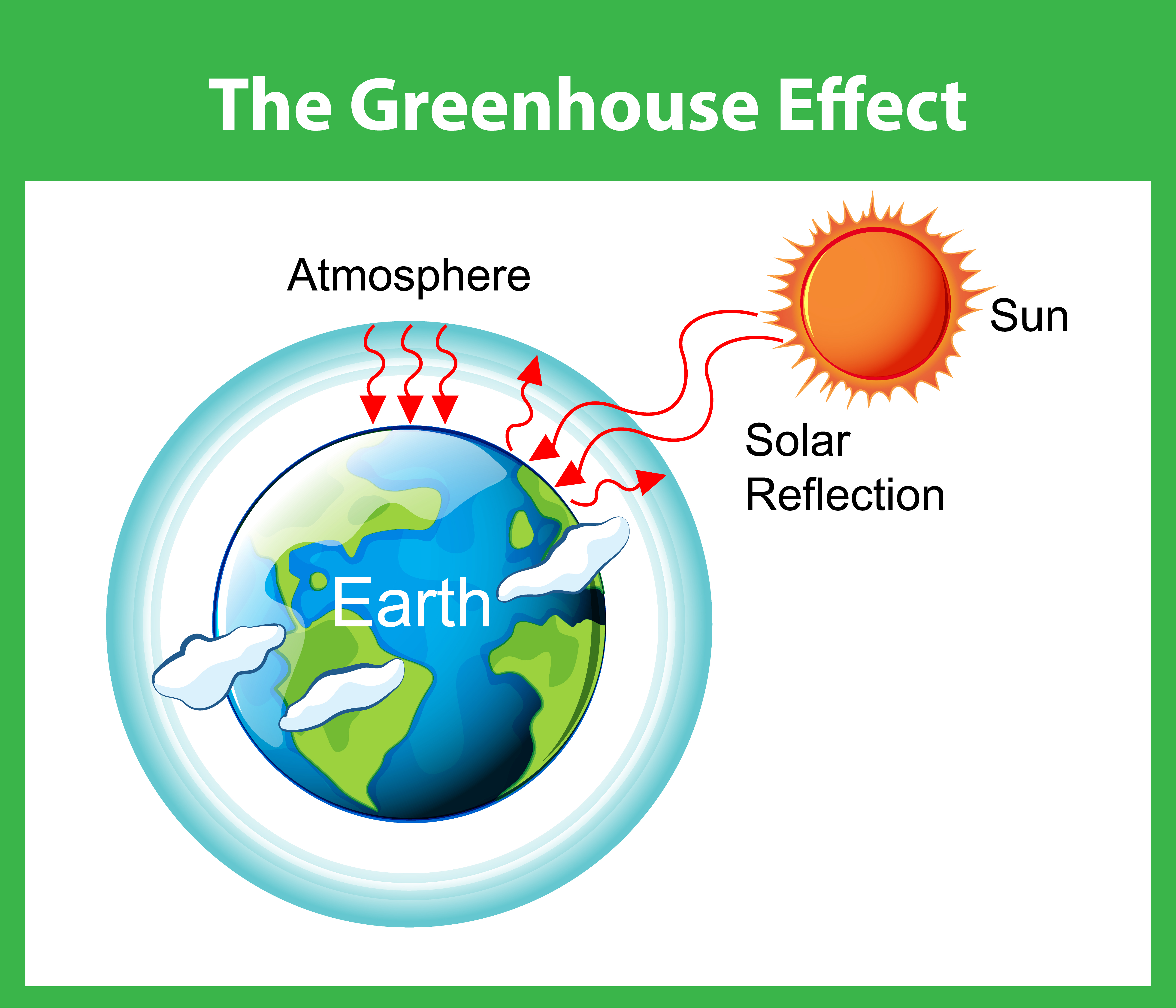



The Greenhouse Effect Diagram Vector Art At Vecteezy
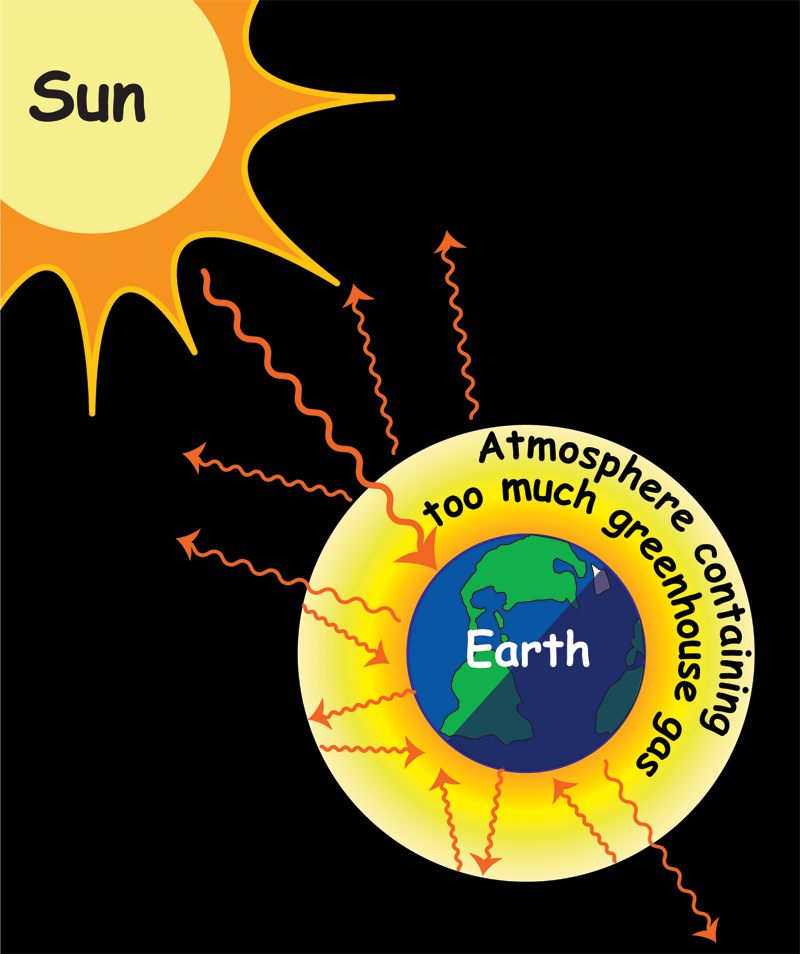



Download Earth Cartoon Drawing




Co2 The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming From The Pioneering Work Of Arrhenius And Callendar To Today S Earth System Models Sciencedirect
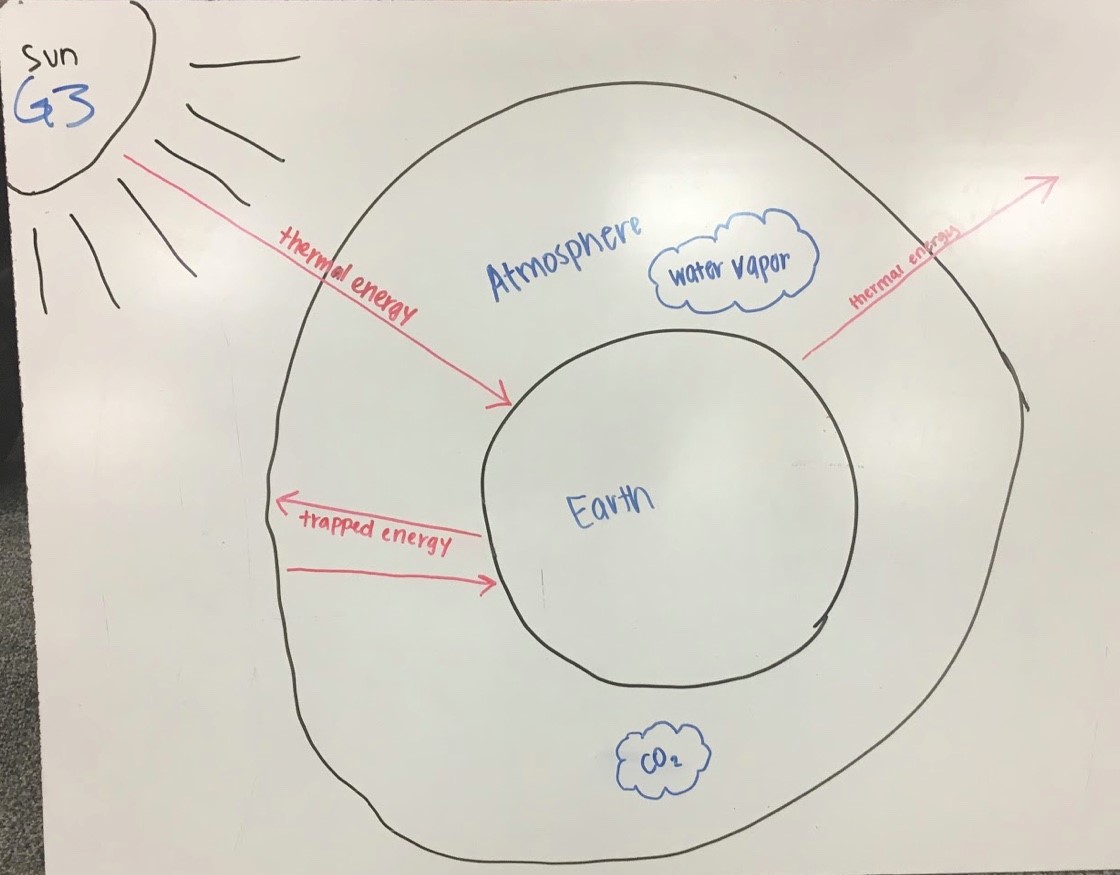



Iv Using Central Ideas About Light And Thermal Phenomena To Explain The Greenhouse Effect Exploring Physical Phenomena
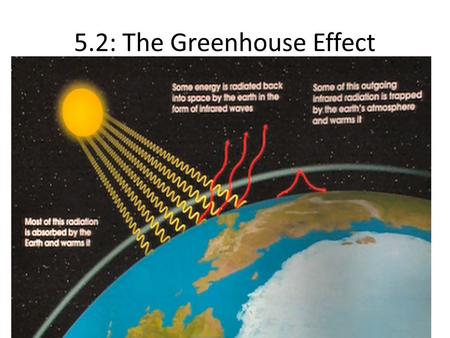



The Greenhouse Effect Draw And Label A Diagram Of The Carbon Cycle Do It Now Ppt Download



Stock Photo Drawing Global Warming Greenhouse Effect Arrow Image Jc Drawing Global Warming Greenhouse Effect Arrow From Sun Stock Photography



5 2 The Greenhouse Effect Biology4ibdp



Q Tbn And9gctaj8wii876qu Vg Qiwf0vbxzn5m2dj2uyfahncczk01qi3 Z7 Usqp Cau



Www Chicagobotanic Org Downloads Nasa Unit 1 Grades 7 9 Activity 1 3 Greenhousegasesnaturalandhumancauses Pdf




The Greenhouse Effect Niwa
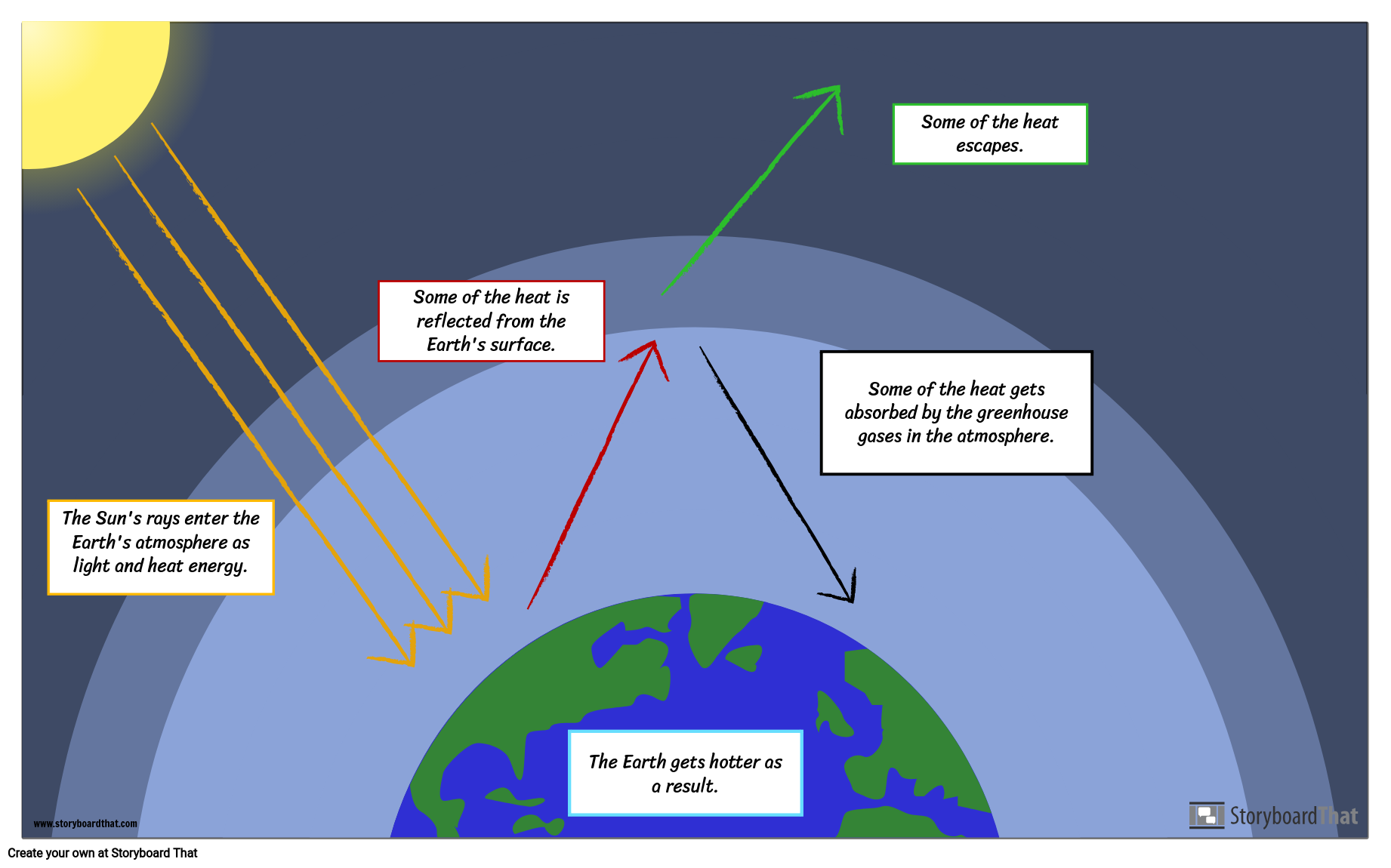



Creating A Greenhouse Effect Diagram




Greenhouse Effect Diagram High Res Stock Images Shutterstock



What Is The Natural Greenhouse Effect And The Anthropogenic Greenhouse Effect What Is The Difference Between Them Quora




Explainer Global Warming And The Greenhouse Effect Science News For Students



Greenhouse Effect Clip Art At Clker Com Vector Clip Art Online Royalty Free Public Domain



Free Greenhouse Gases Cliparts Download Free Greenhouse Gases Cliparts Png Images Free Cliparts On Clipart Library




Draw The Greenhouse Effect Interactive Reading Analysis By Scienceisfun




I Drew The Greenhouse Effect The Sun Illuminates And Warms The Earth Download Scientific Diagram




The Greenhouse Effect Draw And Label A Diagram Of The Carbon Cycle Do It Now Ppt Download



5 2 The Greenhouse Effect Bioninja




Greenhouse Effect Starter Draw What You Think Teaching Resources
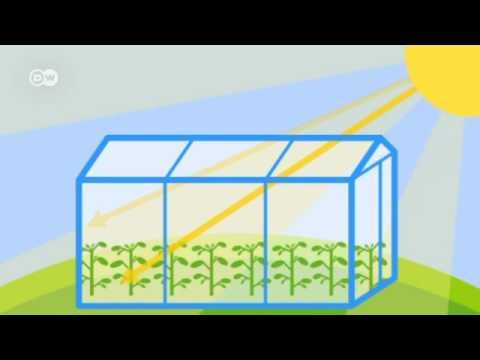



What Is The Greenhouse Effect Global Ideas Youtube




What Is A Greenhouse Page Ppt Download




Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Effect Vs Global Warming Drawing Easy Drawing For Kids Youtube




Vector Layered Paper Cut Style Greenhouse Effect Diagram Global Warming And Climate Change Concept Education Poster Template Canstock
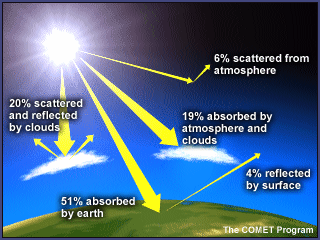



The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases




Greenhouse Effect Diagram High Res Stock Images Shutterstock




Greenhouse Effect Diagram High Res Stock Images Shutterstock




Example Of Student Drawing Based On Textbook Diagram Download Scientific Diagram




Global Warming For Kids A Simple Explanation Of Climate Change
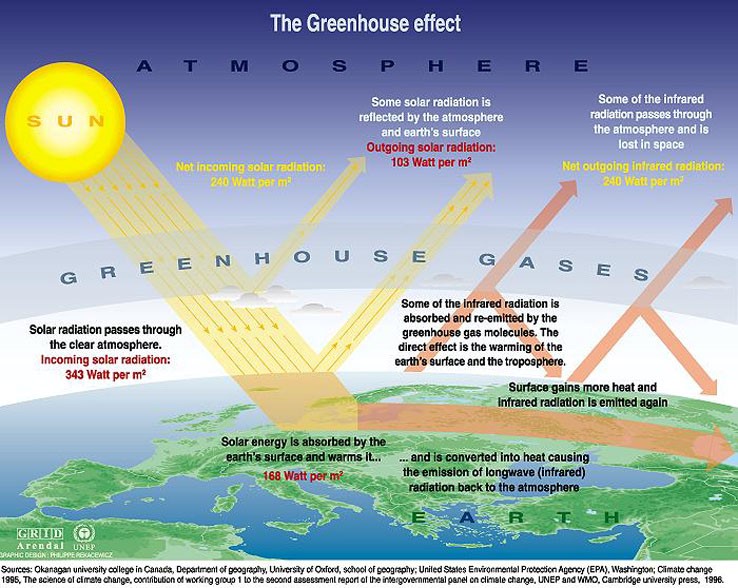



Iv Using Central Ideas About Light And Thermal Phenomena To Explain The Greenhouse Effect Exploring Physical Phenomena




The Greenhouse Effect Easily Understood With A Diagram Help Save Nature



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿